sklearn学习笔记 半监督分类 之 标签传播与SVM的决策边界
“模式识别”研究的问题是如何将不同的事物划分为不同的类别,基于现有的研究,分类识别方法可分为三类:监督识别、非监督识别、半监督识别。1、监督识别需要事先给样本数据集做标签来训练分类器,前期标签数据费时费力;2、非监督识别可根据没有做好标签的样本数据自动生成分类器;3、半监督识别介于监督识别和非监督识别,给一部分样本数据做标签,另一部分不做标签,以此来增强分类器的性能。...
·
“模式识别”研究的问题是如何将不同的事物划分为不同的类别,基于现有的研究,分类识别方法可分为三类:监督识别、非监督识别、半监督识别。
1、监督识别 需要事先给样本数据集做标签来训练分类器,前期标签数据费时费力;
2、非监督识别 可根据没有做好标签的样本数据自动生成分类器;
3、半监督识别 介于监督识别和非监督识别,给一部分样本数据做标签,另一部分不做标签,以此来增强分类器的性能。
比较标签传播(Label Propagation)和 SVM 之间在 sklearn.datasets 自带的 Iris 数据集上生成的“决策边界”。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.semi_supervised import label_propagation # sklearn 自带的半监督
h = .02 # 网格中的步长
# 子图标题
titles = ['Label Spreading 30% data',
'Label Spreading 50% data',
'Label Spreading 100% data',
'SVC with rbf kernel']
iris = datasets.load_iris() # 导入鸢尾花(Iris)数据集
X = iris.data[:, 0:2] # 取数据集前两列特征向量
Y = iris.target # 取数据集的标签(鸢尾花类型)
rng = np.random.RandomState(0) # 设置随机种子
Y_30 = np.copy(Y)
Y_30[rng.rand(len(Y)) < 0.3] = -1
Y_50 = np.copy(Y)
Y_50[rng.rand(len(Y)) < 0.5] = -1
# 由于我们想要绘制支持向量,因此我们不会扩展数据
ls30 = (label_propagation.LabelSpreading().fit(X, Y_30), Y_30)
ls50 = (label_propagation.LabelSpreading().fit(X, Y_50), Y_50)
ls100 = (label_propagation.LabelSpreading().fit(X, Y), Y)
# 创建 rbf 内核的 SVM 分类器,并拟合数据
rbf_svc = (svm.SVC(kernel = 'rbf', gamma = 0.5).fit(X, Y), Y)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
color_map = {-1: (1, 1, 1), 0: (0, 0, .9), 1: (1, 0, 0), 2: (.8, .6, 0)}
for i, (clf, y_train) in enumerate((ls30, ls50, ls100, rbf_svc)):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i + 1) # 创建子图
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap = plt.cm.Paired)
plt.axis('off')
# 绘制训练点
colors = [color_map[Y] for Y in y_train]
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c = colors, edgecolors = 'black')
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.suptitle("Unlabeled points are colored white", Y = 0.1)
plt.show()基于 Anaconda + Jupyter Notebook 环境的运行结果为:
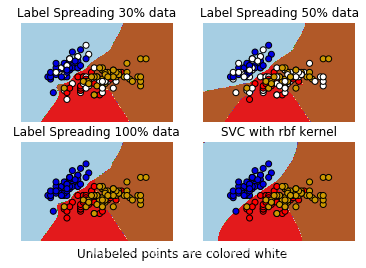
由图可知,即使使用少量的标记数据,Label Propagation 也能学习到良好的边界。
推荐阅读:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)