
【语音增强】匹配滤波器语音识别【含Matlab源码 514期】
匹配滤波器语音识别完整的代码,方可运行;可提供运行操作视频!适合小白!

⛄一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【语音增强】基于matlab匹配滤波器语音识别【含Matlab源码 514期】
点击上面蓝色字体,直接付费下载,即可。
获取代码方式2:
付费专栏Matlab语音处理(初级版)
备注:
点击上面蓝色字体付费专栏Matlab语音处理(初级版),扫描上面二维码,付费29.9元订阅海神之光博客付费专栏Matlab语音处理(初级版),凭支付凭证,私信博主,可免费获得1份本博客上传CSDN资源代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
点击CSDN资源下载链接:1份本博客上传CSDN资源代码
⛄二、匹配滤波器简介
匹配滤波器是一种非常重要的滤波器,广泛应用与通信、雷达等系统中。匹配滤波器的推导数学公式看起来很负责,在通信系统、雷达系统、随机信号处理等很多教科书中都有详细的推导过程。最开始的时候,顺着推导的过程,基本也能推导下来,但对其内在的涵义却无半点认识,可以说完全淹没在公式推导的海洋了。
张直中老师可以说是新中国雷达事业的开拓者之一。就目前的阅读范围来看,张老师在其早期的著作《雷达信号的选择与处理》一书中对匹配滤波器的讲解最为透彻。说句题外话,这本1979年出版的老书,充满了哲学思辨的色彩,让人读起来满口余香,也能让我们充分领略老一辈科学家宽广深厚的学术素养。
所谓的最优滤波器,实际上都是在某个准则下的最优。匹配滤波器对应的最优的准则是输出信噪比(SNR)最大。而且还有一个前提条件是在白噪声背景下。推导很多地方都有,最后的结果就是匹配滤波器的表达式为:
H(f)=S*(f)
也即是说,匹配滤波器的频率响应是输入信号频率响应的共轭。这看起来又很简单,那么如何从物理直观上理解匹配滤波器呢?
一方面,从幅频特性来看,匹配滤波器和输入信号的幅频特性完全一样。这也就是说,在信号越强的频率点,滤波器的放大倍数也越大;在信号越弱的频率点,滤波器的放大倍数也越小。这就是信号处理中的“马太效应”。也就是说,匹配滤波器是让信号尽可能通过,而不管噪声的特性。因为匹配滤波器的一个前提是白噪声,也即是噪声的功率谱是平坦的,在各个频率点都一样。因此,这种情况下,让信号尽可能通过,实际上也隐含着尽量减少噪声的通过。这不正是使得输出的信噪比最大吗?
另外一方面,从相频特性上看,匹配滤波器的相频特性和输入信号正好完全相反。这样,通过匹配滤波器后,信号的相位为0,正好能实现信号时域上的相干叠加。而噪声的相位是随机的,只能实现非相干叠加。这样在时域上保证了输出信噪比的最大。
实际上,在信号与系统的幅频特性与相频特性中,幅频特性更多地表征了频率特性,而相频特性更多地表征了时间特性。匹配滤波器无论是从时域还是从频域,都充分保证了信号尽可能大地通过,噪声尽可能小地通过,因此能获得最大信噪比的输出。
实际上,匹配滤波器由其命名即可知道其鲜明的特点,那就是这个滤波器是匹配输入信号的。一旦输入信号发生了变化,原来的匹配滤波器就再也不能称为匹配滤波器了。由此,我们很容易联想到相关这个概念,相关的物理意义就是比较两个信号的相似程度。如果两个信号完全一样,不就是匹配了吗?事实上,匹配滤波器的另外一个名字就是相关接收,两者表征的意义是完全一样的。只是匹配滤波器着重在频域的表述,而相关接收则着重在时域的表述。
⛄三、部分源代码
function c=melcepst(s,fs,w,nc,p,n,inc,fl,fh)
%MELCEPST Calculate the mel cepstrum of a signal C=(S,FS,W,NC,P,N,INC,FL,FH)
%
%
% Simple use: c=melcepst(s,fs) % calculate mel cepstrum with 12 coefs, 256 sample frames
% c=melcepst(s,fs,‘e0dD’) % include log energy, 0th cepstral coef, delta and delta-delta coefs
%
% Inputs:
% s speech signal
% fs sample rate in Hz (default 11025)
% nc number of cepstral coefficients excluding 0’th coefficient (default 12)
% n length of frame (default power of 2 <30 ms))
% p number of filters in filterbank (default floor(3*log(fs)) )
% inc frame increment (default n/2)
% fl low end of the lowest filter as a fraction of fs (default = 0)
% fh high end of highest filter as a fraction of fs (default = 0.5)
%
% w any sensible combination of the following:
%
% ‘R’ rectangular window in time domain
% ‘N’ Hanning window in time domain
% ‘M’ Hamming window in time domain (default)
%
% ‘t’ triangular shaped filters in mel domain (default)
% ‘n’ hanning shaped filters in mel domain
% ‘m’ hamming shaped filters in mel domain
%
% ‘p’ filters act in the power domain
% ‘a’ filters act in the absolute magnitude domain (default)
%
% ‘0’ include 0’th order cepstral coefficient
% ‘e’ include log energy
% ‘d’ include delta coefficients (dc/dt)
% ‘D’ include delta-delta coefficients (d2c/dt2)
%
% ‘z’ highest and lowest filters taper down to zero (default)
% ‘y’ lowest filter remains at 1 down to 0 frequency and
% highest filter remains at 1 up to nyquist freqency
%
% If ‘ty’ or ‘ny’ is specified, the total power in the fft is preserved.
%
% Outputs: c mel cepstrum output: one frame per row
%
% Copyright © Mike Brookes 1997
%
% Last modified Thu Jun 15 09:14:48 2000
%
% VOICEBOX is a MATLAB toolbox for speech processing. Home page is at
% http://www.ee.ic.ac.uk/hp/staff/dmb/voicebox/voicebox.html
%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
% it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
% the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
% (at your option) any later version.
%
% This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
% but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
% MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
% GNU General Public License for more details.
%
% You can obtain a copy of the GNU General Public License from
% ftp://prep.ai.mit.edu/pub/gnu/COPYING-2.0 or by writing to
% Free Software Foundation, Inc.,675 Mass Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
if nargin<2 fs=11025; end
if nargin<3 w=‘M’; end
if nargin<4 nc=12; end
if nargin<5 p=floor(3log(fs)); end
if nargin<6 n=pow2(floor(log2(0.03fs))); end
if nargin<9
fh=0.5;
if nargin<8
fl=0;
if nargin<7
inc=floor(n/2);
end
end
end
if any(w==‘R’)
z=enframe(s,n,inc);
elseif any (w==‘N’)
z=enframe(s,hanning(n),inc);
else
z=enframe(s,hamming(n),inc);
end
f=rfft(z.‘);
[m,a,b]=melbankm(p,n,fs,fl,fh,w);
pw=f(a:b,:).conj(f(a:b,:));
pth=max(pw(😃)1E-6;
if any(w==‘p’)
y=log(max(mpw,pth));
else
ath=sqrt(pth);
y=log(max(mabs(f(a:b,:)),ath));
end
c=rdct(y).’;
nf=size(c,1);
nc=nc+1;
if p>nc
c(:,nc+1:end)=[];
elseif p<nc
c=[c zeros(nf,nc-p)];
end
if ~any(w==‘0’)
c(:,1)=[];
end
if any(w==‘e’)
c=[log(sum(pw)).’ c];
end
⛄四、运行结果
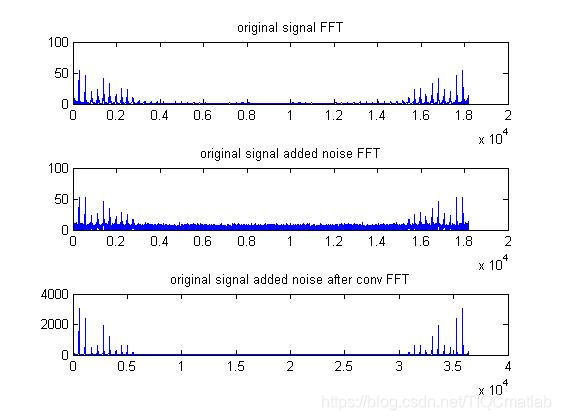
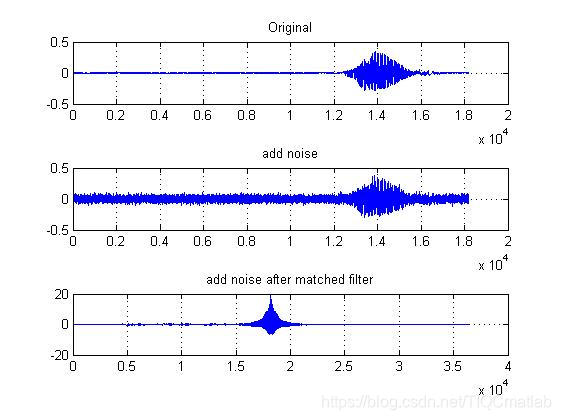

⛄五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]韩纪庆,张磊,郑铁然.语音信号处理(第3版)[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[2]柳若边.深度学习:语音识别技术实践[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
3 备注
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,联系删除
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献11条内容
已为社区贡献11条内容








所有评论(0)